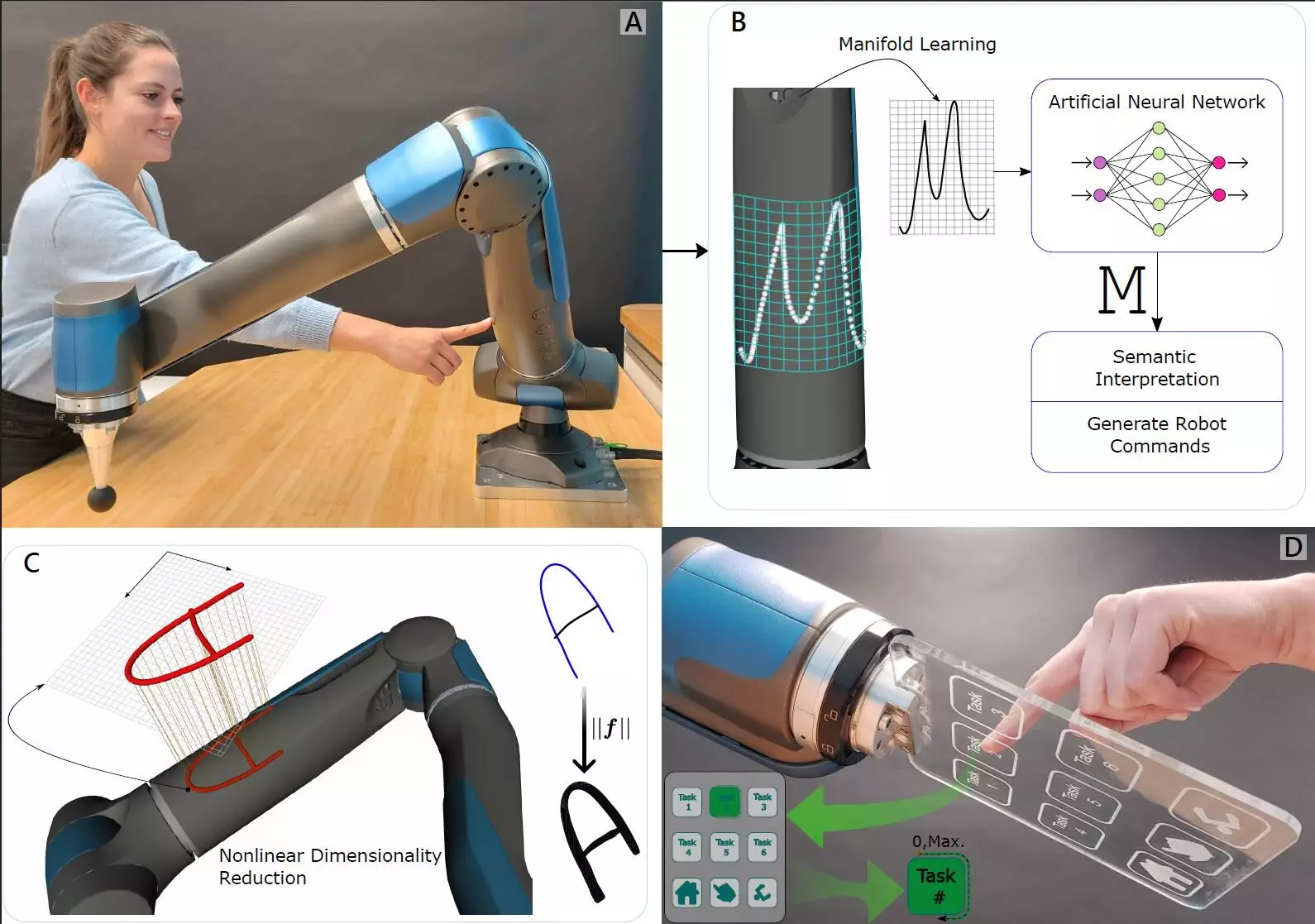
A groundbreaking innovation from the German Aerospace Center’s Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics is reshaping the way we perceive touch in robotics. By integrating traditional internal force-torque sensors with sophisticated machine-learning algorithms, this research underscores a significant shift from the conventional methods that have long been used to endow robots with tactile capabilities. Published in the esteemed journal Science Robotics, this study introduces an approach that not only innovates but also redefines how robots can interact with their environments and humans alike.
Understanding Touch: A Two-Way Interaction
In biology, touch encompasses a rich tapestry of experiences; it is not merely about the sensation one feels upon contact, but it also embodies the capacity to sense when another entity interacts with one’s body. Traditional robotic systems often relied on artificial skin technology, a method that, while innovative, has limitations in efficiency and adaptability. The research team’s novel solution involved imparting a robot with the capability to understand touch through an internal perspective—much like how humans experience pressure through their joints. By recognizing the torque generated at the joints during contact, the robot can effectively gauge varying degrees of touch from external sources, revealing a nuanced understanding of environmental interactions.
Technological Implementation: An Ingenious Method
The genius of this approach lies in its simplicity and focus on enhancing the robot’s existing frameworks rather than building entirely new sensory skins. By positioning highly sensitive force-torque sensors in the joints of a robotic arm, the researchers enabled the robot to detect multidirectional pressure. The next step—utilizing machine learning—was crucial. By training algorithms to decode and interpret the data gathered from these sensors, the robot gained an unprecedented level of sensitivity, allowing it to distinguish when a finger pressed upon a specific location on its arm. The ability to recognize various aspects of touch, such as pressure and location, opens a plethora of interactive possibilities.
Implications for Human-Robot Interaction
The ramifications of this development extend beyond mere novelty; they signify a paradigm shift in human-robot collaboration, particularly in industrial settings. As robots become increasingly integrated into our workplaces, crafting machines that can “feel” their environment fosters safer and more intuitive interactions. Robots equipped with this technology could operate alongside human co-workers with a deeper understanding of their presence, leading to enhanced safety, efficiency, and productivity on the factory floor.
Moreover, the research could pave the way for more emotionally intelligent robots capable of sensing not only the physical presence of humans but also the subtleties of touch that convey intent and comfort. In environments where human-robot interaction is commonplace, such as caregiving or education, the potential applications of this technology could redefine how we view machine empathy and responsiveness.
This innovative fusion of robotics and artificial intelligence represents not just a technical achievement, but a significant leap toward more empathetic and interactive technological companions. As robots gain a more human-like sensitivity, the possibilities for their integration into varied sectors of society become boundless, heralding a new era in the evolution of intelligent machines.